In the ever-evolving landscape of digital file management, WinZip continues to lead the way with leading encryption and compression technology.
In our commitment to enhancing our customer experience, we’ve worked hard over the past several product releases to streamline workflows and modernize the software.
In this article, we’ll show you:
- Modern account portal
- Simplified navigation ribbon
- Enhanced WinZip Courier
- WinZip home screen
- Enhanced SafeShare
- Enhanced Secure Backup
- Enhanced PDF Express
- Simultaneous unzipping of multiple files
- New Secure FTP (SSH) file transfer
Streamline your workflow with an updated account portal
The first up is the WinZip account portal, recently introduced in September 2023.
With the new account portal, users gain unprecedented control and accessibility, empowering them to manage their account, user profile, and software subscriptions.
This feature streamlines workflow and enhances collaboration and data security, marking a significant leap forward in the WinZip experience.
Since the WinZip account portal is cloud-based, updates are rolled out dynamically on a regular basis.
Here are notable new key features implemented since our initial release:
- New and enhanced products page aimed at improving the subscription experience.
- Improved license compliance within our suite products.
- Updated subscriptions page with enhanced functionality and clarity.
Simplified navigation ribbon to toggle between simplified and advanced ribbon interface
With our new simplified navigation ribbon, users can easily toggle between a simplified and advanced toolbar, tailoring the WinZip experience to individual needs.
The simplified ribbon grants quick access to commonly used features, maintaining a clean and clutter-free UI, while the advanced ribbon ensures access to the full suite of WinZip features, providing familiarity and flexibility.

Send emails and attachments of any size with WinZip Courier
With our newly modernized WinZip Courier, users can send emails and attachments of any size safely and securely with leading encryption technology. This is used in industries where sending encrypted emails and large attachments is critical.
Expanding upon the fresh, modern aesthetic of WinZip Courier, the latest update further enhances the user experience by offering enhanced control over Courier’s settings.
It streamlines the process of securely transferring files via email, ensuring a smoother and more efficient workflow.
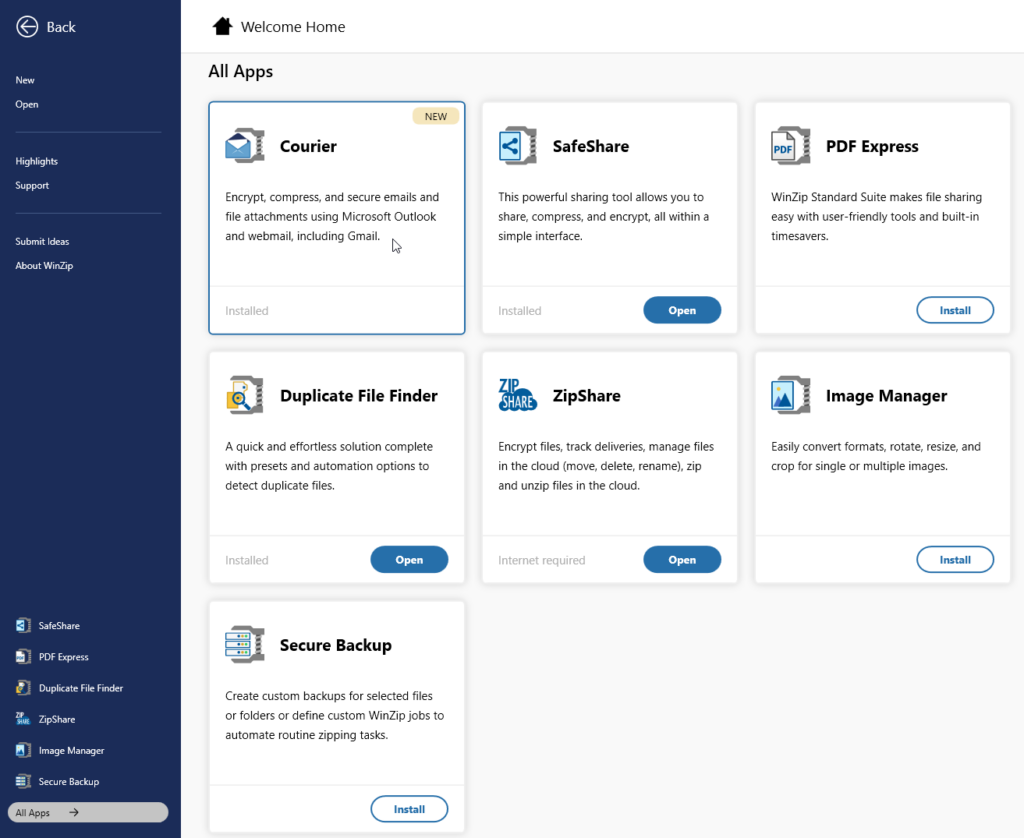
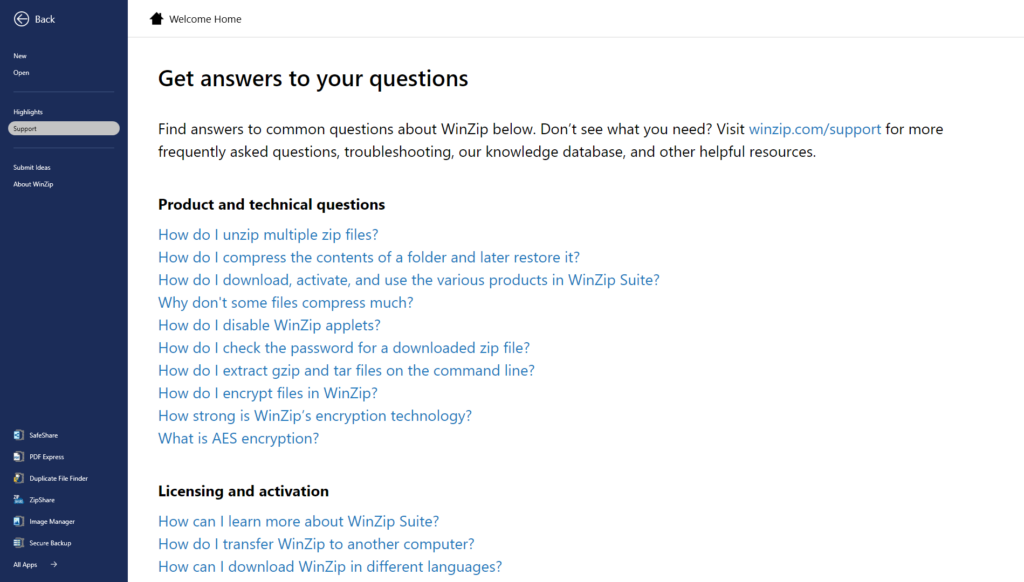
New WinZip home screen gives you direct access to all your apps
The new WinZip home screen enhances the user experience by providing direct access to productivity apps, in-app support, and a wealth of valuable resources — all in one convenient location.
Ensure maximum security with SafeShare
Enhanced SafeShare simplifies file sharing while ensuring maximum security, making collaboration effortless and worry-free. It features an intuitive drag-and-drop interface, so users can instantly share large files simply and safely.
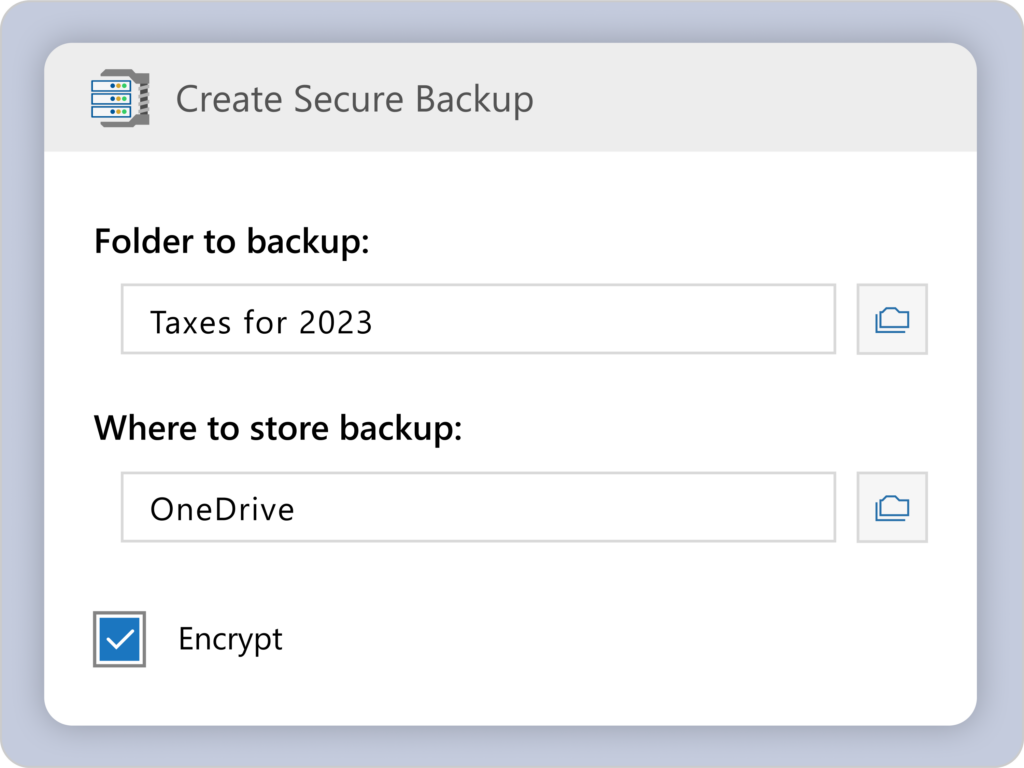
Give yourself peace of mind with Secure Backup
Enhanced Secure Backup provides peace of mind by safeguarding critical data against loss or compromise. Users can create automated backups of critical files in just a few clicks.
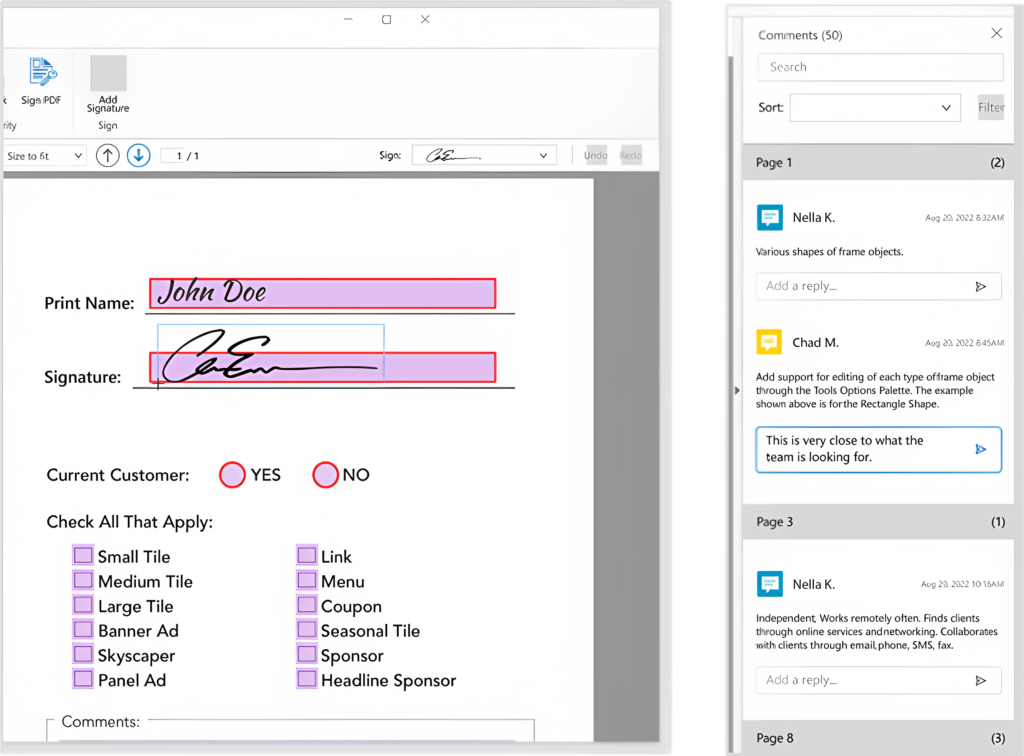
Enhanced PDF Express lets you handle digital documents with ease
Enhanced PDF Express streamlines the creation and editing of PDF documents, empowering users to handle their digital documents with ease.

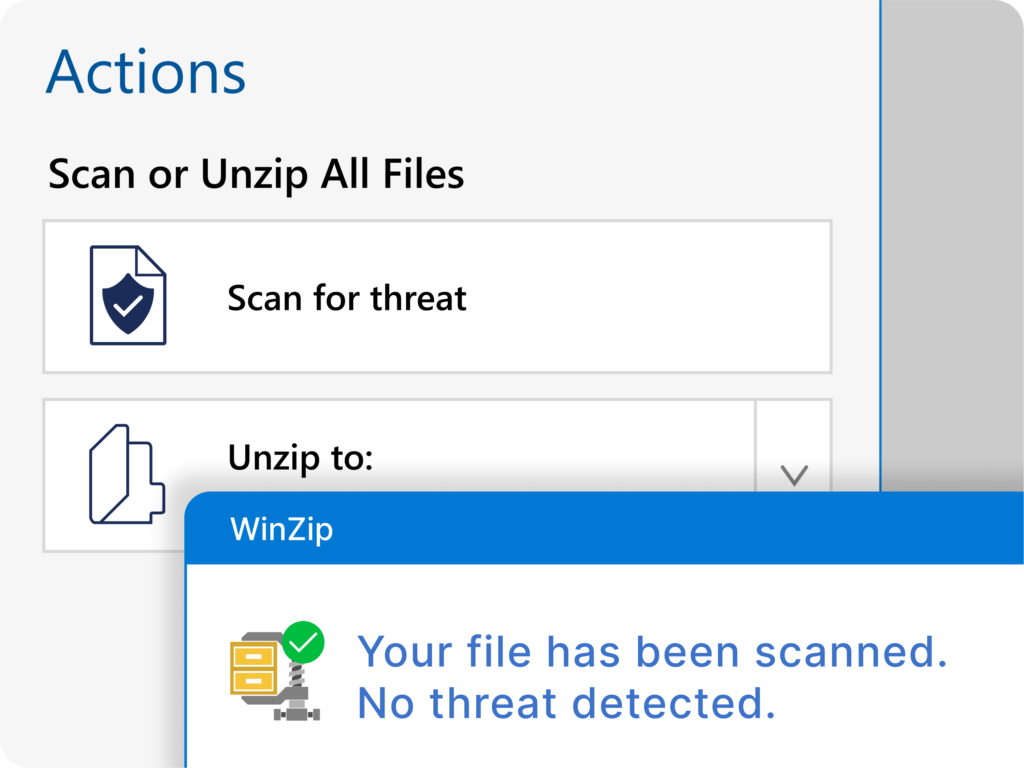
Unzip multiple files at one time
But the latest release doesn’t stop there—it also enhances productivity with the ability to unzip multiple files simultaneously within WinZip.
Save time and effort by batch extracting files directly to your desired locations, simplifying your workflow.
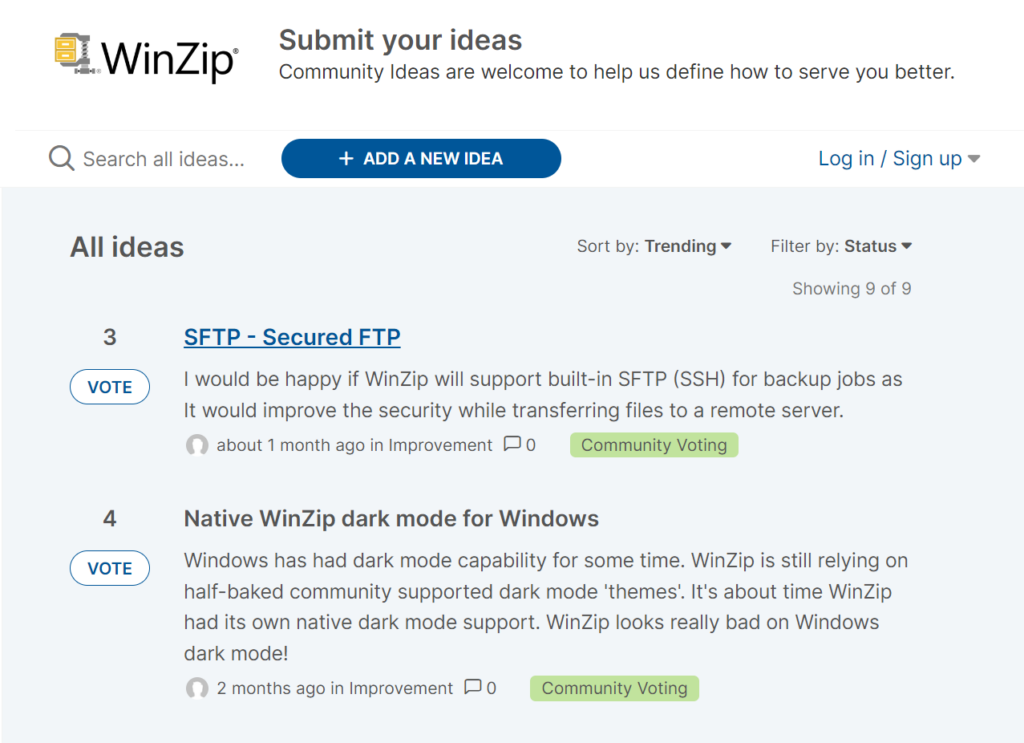
New Secure FTP with a compliant environment
Additionally, the inclusion of Secure FTP (SSH) file transfer—a top-rated idea from our ideas portal—provides a secure and compliant environment for entities with stringent data security protocols.
This latest release represents a culmination of our dedication to innovation and user-centric design.
From modernization efforts aimed at enhancing usability to features designed to streamline workflows and bolster security, this release embodies our commitment to empowering users with the tools they need to succeed in today’s digital age.
Want to learn more about the latest release of WinZip? Read more about the latest features now.
Download a free trial of WinZip today and unlock a new level of efficiency in file management and data security.