Over the last few decades, the healthcare industry has embraced technology to enhance patient care, streamline operations, and store vast amounts of sensitive patient data electronically. However, with these advancements comes a pressing concern: healthcare data security challenges.
The healthcare sector is a prime target for cybercriminals due to the immense value of patient information, including personal, financial, and medical records. One of the primary challenges is the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, ranging from ransomware attacks to data breaches, which can compromise patient confidentiality and trust.
Moreover, the interconnected nature of healthcare networks and the diverse range of devices used to access patient data introduce vulnerabilities requiring comprehensive security measures to protect against internal vs. external security threats.
WinZip® Enterprise recently conducted a survey to better understand the importance of data security at organizations. Amongst many other findings, the report shows that 79% of respondents said their organization works with personally identifiable information (PII), payment card information (PCI), or personal health information (PHI). This highlights the critical need for healthcare organizations to safeguard sensitive data from internal and external security threats.
This article explores some of the most common healthcare data security challenges and discusses potential strategies to mitigate risks and safeguard patient information in this ever-evolving landscape. By addressing internal and external security threats, healthcare organizations can strengthen their data protection efforts and ensure the confidentiality and integrity of patient data.
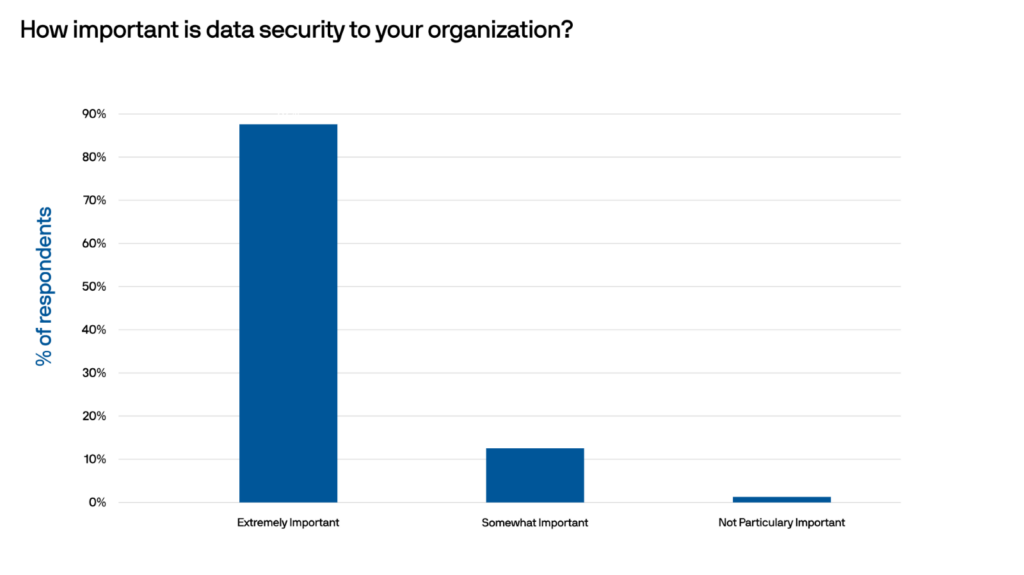
The importance of data security in healthcare
Healthcare information holds immense value to hackers and malicious actors due to the sensitive nature of the data. Internal vs. external challenges can be equally damaging to a business.
Given the potentially devastating consequences of healthcare data breaches, healthcare organizations must invest in robust cybersecurity measures, employee training, and strict data protection policies to safeguard patient information and maintain public trust.
Here are some reasons why healthcare information is a prime target for cybercriminals:
- Personal Identifiable Information (PII). Healthcare records typically contain a wealth of personal identifiable information, such as names, addresses, social security numbers, and insurance details. This information can be exploited for various identity theft schemes, leading to financial fraud or creating fake identities.
- Financial gain. Stolen healthcare data can be sold on the dark web to other cybercriminals for significant sums of money. This data is highly sought after by individuals or groups involved in illegal activities, including insurance fraud, pharmaceutical scams, and illegal prescription drug sales.
- Medical fraud. Medical records can be manipulated or used to submit fraudulent insurance claims for treatments or procedures that never occurred. This defrauds insurance companies and can lead to incorrect treatments being administered to patients.
- Ransomware attacks. Hospitals and healthcare facilities are particularly susceptible to ransomware attacks, where hackers encrypt critical patient data and demand a ransom to unlock it. The urgency of patient care makes healthcare institutions more likely to pay the ransom to regain access to their data quickly.
- Espionage and sabotage. Nation-states or competing healthcare organizations may attempt to steal valuable medical research, proprietary information, or sensitive government data to gain a competitive advantage or for political reasons.
- Lack of cybersecurity awareness. Sometimes, healthcare organizations may not prioritize cybersecurity adequately, leaving vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit to gain unauthorized access to systems and databases.
- Long-term value. Unlike credit card data, which may quickly become obsolete, healthcare data has long-term value. Medical histories, prescription records, and lab results remain valuable for years, making them an attractive target for cybercriminals.
Types of healthcare data (and their value)
Healthcare organizations handle various types of data, each of which holds significant value to malicious actors due to their sensitivity and potential for exploitation. Some of the different types of healthcare data and their value to attackers include:
Personal Identifiable Information (PII):
- Includes names, addresses, dates of birth, social security numbers, and contact information.
- Valuable for identity theft, financial fraud, and social engineering attacks.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs):
- Contains comprehensive patient health information, medical history, diagnoses, treatments, and medications.
- Can be sold on the black market for various purposes, such as insurance fraud, medical identity theft, or targeted phishing attacks.
Protected Health Information (PHI):
- Encompasses health information that can be linked to a specific individual, including lab results, medical images, and genetic data.
- Valuable for medical research, insurance fraud, blackmail, or extortion.
Financial Information:
- Includes billing records, insurance details, and payment information.
- Useful for financial fraud, false insurance claims, or fraudulent medical billing schemes.
Medical Device Data:
- Data collected by medical devices, such as pacemakers or insulin pumps.
- Can be exploited to harm patients, conduct ransomware attacks, or steal sensitive medical information.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Research Data:
- Valuable medical research findings, drug development data, or proprietary healthcare technologies.
- Valuable for corporate espionage or selling to competitors.
Credential Information:
- Usernames, passwords, and access credentials for healthcare systems and databases.
- Enables unauthorized access, data breaches, and lateral movement within the organization’s network.
Malicious actors target healthcare data due to its high value on the black market and its potential to cause significant harm to individuals and organizations.
Protecting this data is crucial to ensure patient privacy, maintain trust, and prevent the potential consequences of data breaches and cyberattacks in the healthcare sector.
The cost of healthcare-related security breaches
Historically, healthcare-related security breaches have been among the most expensive compared to breaches in other industries. According to IBM Security’s 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of a healthcare data breach was $11 million in 2022, a $1 million increase from the year before.
The report also shows that the global average cost of a data breach across all sectors in 2023 was just $4.45 million. This number is a 15 percent increase over the last three years, but this is just a fraction compared to healthcare data breach costs.
Healthcare security breaches can lead to significant financial repercussions, including fines and other costs. These often differ from other industries due to the unique regulatory landscape and the sensitive nature of the data involved.
Some of the financial impacts of a data security breach at a healthcare organization can include:
Regulatory fines
Healthcare organizations are subject to strict data protection regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. If a breach occurs and it is found that the organization failed to comply with these regulations, it can face substantial fines.
In the U.S., HIPAA violations can result in penalties ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million for each law violation provision. Similarly, a GDPR lower-level violation in the EU can result in fines of up to $11.03 million (or two percent of the company’s annual revenue), whichever is greater.
Such fines can quickly escalate depending on the scale of the breach and the number of individuals affected.
Legal settlements and lawsuits
A healthcare data breach can lead to a flood of lawsuits from affected patients or individuals whose data was compromised. These lawsuits can seek damages for negligence, emotional distress, or medical identity theft.
The costs associated with legal settlements can be significant and vary depending on the severity of the breach and the number of affected individuals.
Reputation damage
Healthcare breaches can erode public trust and damage the reputation of the affected organization. The loss of trust can result in reduced patient visits, decreased revenue, and the loss of business partnerships, further impacting the organization’s bottom line.
Notification and remediation costs
Healthcare organizations are legally required to notify affected individuals and regulatory authorities promptly after a breach. This process involves communication expenses, credit monitoring services for affected individuals, and the implementation of measures to remediate the breach and prevent future incidents.
Operational disruptions
A significant breach can disrupt normal healthcare operations, leading to temporary closure of facilities, cancellation of appointments, and downtime for staff. These operational disruptions can result in revenue losses and additional expenses to restore normalcy.
Cybersecurity enhancements
Following a breach, healthcare organizations may be required to invest in additional cybersecurity measures to prevent future incidents. These can include advanced security systems, employee training, and regular security audits, adding to the overall cost burden.
How to mitigate data security risks at healthcare organizations
To mitigate internal and external security risks, you need to know what to look for and how to protect your business.
When healthcare organizations seek to mitigate security threats and maintain compliance with industry regulations, they should focus on the following key factors:
- Data encryption and security. Implement robust data encryption measures to protect sensitive patient information in transit and at rest. Encryption ensures that it remains unreadable and secure even if data is intercepted or compromised.
- Access controls and authentication. Employ strong access controls and authentication mechanisms to limit data access only to authorized personnel. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to verify users’ identities.
- Regular employee training. Conduct security awareness training for all employees to educate them about potential threats, phishing attacks, and best practices for handling sensitive data.
- Incident response plans. Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to swiftly and effectively respond to security incidents, minimize damage, and recover normal operations.
- Compliance with industry regulations. Stay updated with healthcare-specific regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, or regional laws, and ensure full compliance to avoid penalties and fines.
- Vendor assessment. If third-party vendors are involved, perform thorough security assessments to ensure they meet required security standards and safeguard patient data.
- Continuous monitoring and auditing. Implement continuous monitoring and regular security audits to proactively identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
WinZip Enterprise can play a role in securing data. However, our software is just one piece of the overall security strategy. Healthcare organizations should adopt a holistic approach, incorporating specialized security solutions and best practices to safeguard patient information effectively.
With WinZip, healthcare organizations can:
- Encrypt files with robust encryption algorithms.
- Securely transfers files containing sensitive data using secure transfer methods, such as SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) or encrypted email services.
- Protect and set strong passwords to ensure only authorized individuals can access the data.
- Limit access to Zip files containing sensitive data only to individuals who genuinely need it.
Interested in hearing more about our report’s findings? Click here for access to the full report!

